Introduction to the Competition Games: Monopoly Pricing and Sunk Costs
Pedagogic Purpose:
- Introduce the competition games.
- Illustrate the trade-off between margins and sales.
- Introduce marginal reasoning.
- Have students discover the impact of sunk costs on incentives.
Duration: 10 minutes.
Context:
Players are in a monopoly position and must select their price on 2 identical markets: On each market, the marginal cost of production is constant and equal to 4€ and players can sell up to 1000 goods on each market. What differs is that on the second market, there is a sunk cost equal to 35000€. The game is repeated.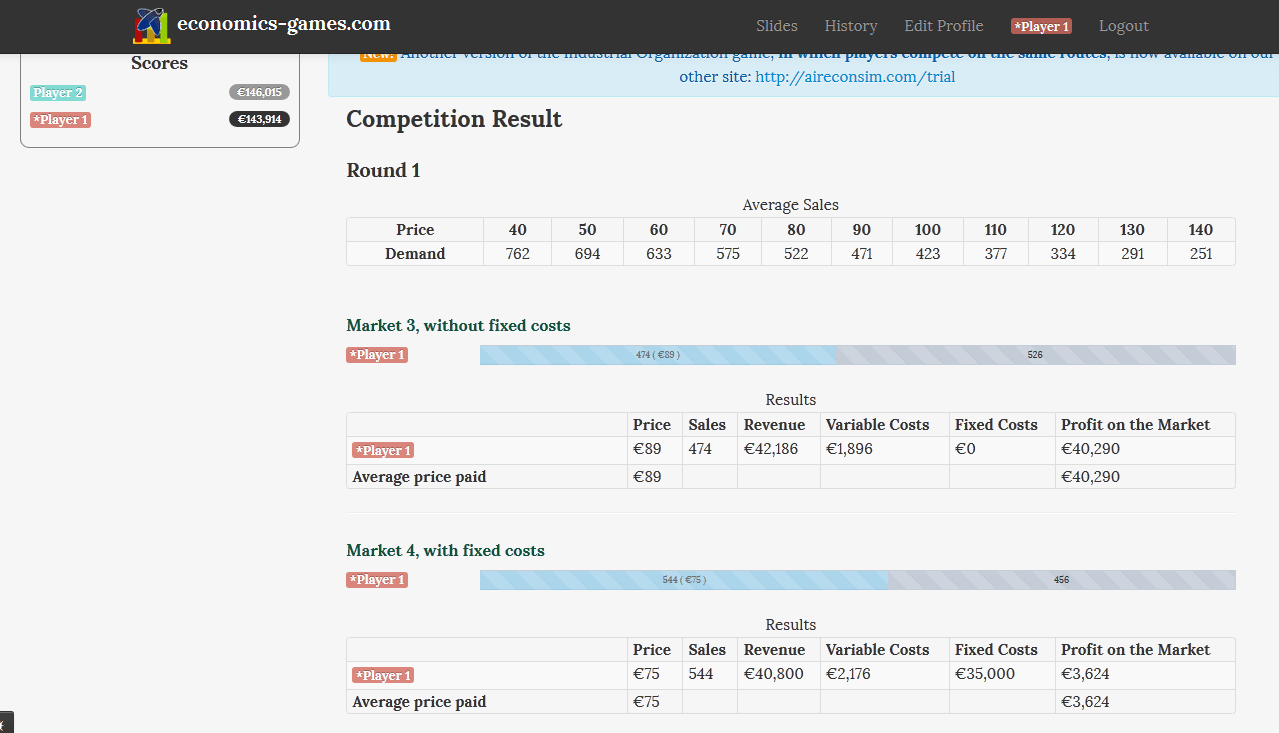
What happens in the game?
This game can seem obvious, but it is very effective as an introduction to sunk costs and monopoly pricing.- If players do not realize from the start that the optimal price is the same on both markets, they will soon come to understand this by tatonnement.
- By changing their price from one round to the other, they find themselves in a situation where marginal reasoning is perfectly natural.
- This game provides a monopoly benchmark for later games (monopoly price~€96, monopoly profit net of sunk costs: ~€40680), as demand is the same in all games (proportionally to the number of players on the markets).
- Even if this is not so fun, players will do it carefully in order to prepare for later multiplayer games and get accustomed to the demand function (provided that it does not last too long).
Possible theoretic debriefings
- Impact of sunk costs on the ranking of alternatives.
- Notion of marginal Revenue, decreasing marginal revenue and marginal cost.
- Illustrates the interest of marginal reasoning through the iterative search for the monopoly price (potential debrief with demand data).
- Cost pass-through (the monopoly price with a €4 marginal cost is only €2 higher than the revenue maximizing price).
For more information about demand or about how to use this game within a sequence of market games:
Rules as explained to players:
- You are in a monopoly position on 2 identical markets: On each market, the marginal cost of production is constant and equal to 4€, the maximal production capacity is equal to 1000 goods (specific to that market).
-
Demand on each market is such that:
- If you charge a price equal to 50€,you will sell about 694 goods.
- If you choose a price equal to 40€, you will sell about 762 goods.
| Price | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 | 130 | 140 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demand | 762 | 694 | 633 | 575 | 522 | 471 | 423 | 377 | 334 | 291 | 251 |
- What differs is that on the second market, there is a sunk cost equal to 35000€.
- On the first market, your total cost if you sell q goods is €4*q, on the second market it is equal to €35000 +4*q.
- Your goal is to maximize your company's profit, not to beat your competitors nor to sell the maximum number of goods (and anyway your final ranking will be determined by comparing your profit against every other players, some of which compete in different "universes")